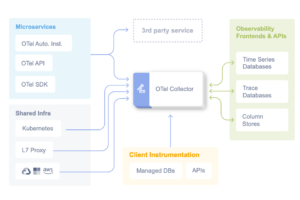
The OpenTelemetry community has released version 1.49.0/v0.143.0 of the OpenTelemetry Collector on January 5-6, 2026, bringing significant updates to the world’s most popular open-source observability framework. As OpenTelemetry continues its rapid adoption—with 48.5% of organizations already using it and another 25% planning to implement it—this release reinforces OpenTelemetry’s position as the de facto standard for modern observability.
Key Updates in OpenTelemetry Collector v1.49.0
Semantic Conventions Upgrade to v1.38.0
The latest release updates OpenTelemetry semantic conventions to version 1.38.0, ensuring better standardization across instrumentation libraries and frameworks. Semantic conventions define how telemetry data should be structured and labeled, making it easier for teams to correlate metrics, logs, and traces across different services and vendors.
Profiles Support in Nop Exporter
OpenTelemetry v1.49.0 adds profiles support to the nop exporter, expanding the framework’s capabilities beyond traditional metrics, logs, and traces. Continuous profiling data helps development teams identify performance bottlenecks at the code level, complementing distributed tracing for comprehensive application performance monitoring.
OTLP Protobuf Upgrade to v1.9.0
The OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP) protobuf definitions have been upgraded to version 1.9.0, bringing improved data serialization and compatibility across OpenTelemetry SDKs and collectors. This ensures better interoperability as more vendors adopt OTLP as their native ingestion format.
Performance Optimizations
This release includes important performance improvements with optimized pdata struct sizes and enhanced pointer handling. These optimizations reduce memory overhead and improve throughput for high-volume telemetry collection, critical for organizations processing millions of spans and data points per second.
Breaking Changes: What You Need to Know
Required Telemetry Field
Important: The otelcol.Factories.Telemetry field is now required in v1.49.0. Previously, if this field wasn’t set, it would default to an otelcol telemetry factory. Callers of the otelcol package must now set this field explicitly when building custom collector distributions.
Entity Method Renaming
OpenTelemetry has renamed Entity methods to align with specification terminology:
Entity.IDAttributes() → Entity.IdentifyingAttributes()
Entity.DescriptionAttributes() → Entity.DescriptiveAttributes()Update your code accordingly to maintain compatibility with the latest collector version.
Pointer Receivers in xprocessor
The xprocessor factory methods now use pointer receivers for consistency with other factory implementations. This change improves code maintainability across the OpenTelemetry Collector codebase.
OpenTelemetry Collector Contrib Updates
The community-maintained Collector Contrib repository also received several important updates:
Deprecated Configuration Removal
The Prometheus receiver has removed long-deprecated configuration options use_start_time_metric and start_time_metric_regex. Teams should review their collector configurations to ensure they’re not using these legacy settings.
Enhanced Tail Sampling
Tail sampling now supports caching the policy name involved in sampling decisions. This allows the tailsampling.policy attribute to be set on spans when a sampling decision is cached, improving observability into your sampling strategy.
Cloud Platform Log Parsing
Google Cloud logging extensions now parse Cloud DNS Query and Cloud Armor logs into structured log record attributes, rather than placing raw data in the message body. This makes Cloud Platform logs more queryable and actionable.
Known Issues: OCB and OpAMPSupervisor
The v0.143.0 release encountered issues with the OpenTelemetry Collector Builder (OCB) and OpAMPSupervisor artifacts. Due to a broken release script and subsequent complications, these components weren’t released in v0.143.x. Since there are no changes between v0.142.0 and v0.143.0 for these tools, teams can safely use:
- OCB v0.142.0 with v1.49.0/v0.143.0 components
- Both artifacts will be released in the upcoming v0.144.0 version
OpenTelemetry’s Growing Momentum in 2026
Adoption Accelerating Across Industries
OpenTelemetry has reached a tipping point in 2026. Industry data shows:
- 48.5% of organizations currently use OpenTelemetry
- 25% are actively planning implementation
- 61% of users consider OTel “Very Important” or “Critical”
- 81% believe OpenTelemetry is production-ready
- 90%+ greenfield adoption expected for new projects
Why Organizations Choose OpenTelemetry
Vendor Neutrality: OpenTelemetry instrumentation works with any observability backend, eliminating vendor lock-in and giving organizations negotiating leverage on pricing.
Cost Optimization: Teams report significant cost reductions—STCLab achieved 72% cost savings while moving from 5% sampled traces to 100% APM coverage across all environments.
Standardization: By standardizing instrumentation across languages and signal types (metrics, logs, traces, and now profiles), OpenTelemetry removes friction for development teams and enables new observability vendors to enter the market more easily.
Future-Proofing: As a CNCF graduated project with 10,000 contributors from 1,200 companies, OpenTelemetry represents the industry consensus on how observability should work in cloud-native environments.
OpenTelemetry Adoption in 2026
Industry Data Shows Rapid Growth and Maturity
Current Adoption Status
User Sentiment & Readiness
OpenTelemetry vs. Proprietary APM: The New Reality
Traditional APM vendors face increasing pressure as OpenTelemetry becomes the default instrumentation layer. The economic advantages are compelling:
With OpenTelemetry:
- Collect 100% of traces with intelligent sampling
- Multi-tier storage strategies (hot data vs. cold archives)
- Switch backends without re-instrumentation
- Negotiate better rates with portable data
Without OpenTelemetry:
- Vendor-specific agents with sampling imposed at collection
- Single storage tier at premium pricing
- Migration requires full re-instrumentation
- Limited pricing negotiation leverage
What This Means for DevOps and Platform Teams
Skill Requirements Evolving
Job postings increasingly require OpenTelemetry experience. Universities are incorporating OTel into DevOps curricula. Platform engineering teams need deep understanding of:
- Collector configuration and pipeline design
- Sampling strategies (head-based vs. tail-based)
- Data tiering and retention policies
- OTLP protocol and semantic conventions
FinOps Integration
Organizations are treating observability costs as a first-class concern, with:
- Pre-deployment cost gates that reject services generating excessive telemetry
- Chargeback models making costs visible to product teams
- Platform-enforced cost budgets
- AI-driven optimization adjusting sampling rates based on system health
Looking Ahead: OpenTelemetry in Q1 2026
The OpenTelemetry community continues rapid development with several initiatives:
OTel Unplugged EU comes to Brussels on February 2, 2026—an unconference event following FOSDEM, where the community gathers to discuss implementation challenges, share patterns, and shape the project’s future.
Democratizing Observability: The focus for 2026 extends beyond technical capabilities to usability. Vendors are building on OpenTelemetry’s standardization to deliver consistent, out-of-the-box insights without requiring heavily customized dashboards. The goal: make observability accessible beyond the in-house expert.
AI-Powered Observability: The combination of standardized OpenTelemetry data and AI capabilities enables automated root-cause analysis, predictive anomaly detection, and intelligent sampling. OpsPilot and similar AI-powered observability platforms translate OTLP data into actionable insights, diagnosing complex system issues in seconds rather than the typical 30-45 minutes of manual investigation.
Upgrade Recommendations
If you’re running OpenTelemetry Collector:
- Review breaking changes: Check if your custom collector distributions or processors use the renamed Entity methods or require explicit Telemetry field configuration
- Update Prometheus configuration: Remove deprecated use_start_time_metric and start_time_metric_regex settings
- Test before production: Deploy v1.49.0 in staging environments to validate compatibility
- Monitor performance: The pdata optimizations should improve throughput—track metrics to quantify improvements
- Plan for v0.144.0: If you use OCB or OpAMPSupervisor, continue with v0.142.0 until the next release
Conclusion: OpenTelemetry’s Path Forward
OpenTelemetry v1.49.0 represents continued maturation of the observability standard. While it may not single-handedly “save” observability from complexity and cost challenges, OpenTelemetry is fundamentally changing what’s possible by:
- Lowering barriers to entry for new observability solutions
- Enabling cost optimization strategies proprietary agents can’t support
- Creating a foundation for consistent, reusable observability across teams
- Empowering vendors to focus on insights rather than instrumentation
As organizations navigate the observability cost crisis and rising system complexity, OpenTelemetry provides the standardization and flexibility needed to build sustainable, scalable monitoring solutions. The 2026 roadmap promises continued innovation in usability, AI integration, and cross-signal correlation—all built on the solid foundation of open standards.
About OpsPilot: The next-generation OpsPilot platform leverages OpenTelemetry to deliver AI-powered observability intelligence. We translate OTLP data into actionable insights, helping teams diagnose complex system issues in seconds. Learn more about our OTel-native approach to modern observability.
Resources: